
What Is the Difference Between a BA and a BS Degree?
The Bachelor of Arts (BA) and the Bachelor of Science (BS) are undergraduate degrees you can earn to help elevate your career and develop relevant job skills. Although programs vary depending on the school, BS degrees typically have more coursework in subjects such as science, math, and technology, while BA degrees tend to focus more heavily on the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
With a bachelor’s degree, you may qualify for more roles and see other benefits, such as higher salaries, but it is a significant investment. Understanding the different types of programs is important in making an informed decision. In this article, we'll go over the differences between the two degrees, and how you can determine which is best for you.
BA vs. BS degrees: What’s the difference?
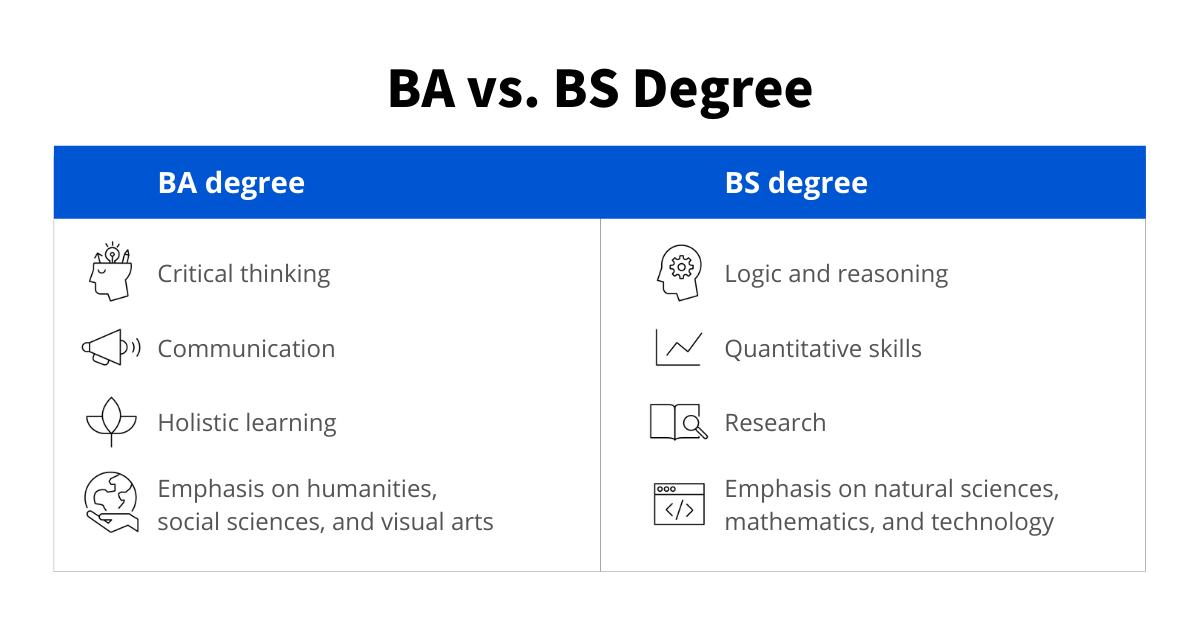
The main difference between the BA and the BS is the subject matter. BA degree coursework tends to focus on critical thinking, communication, and holistic learning, whereas BS degree coursework tends to focus on logic, reasoning, and quantitative skills. Otherwise, the two are not that different. In most cases, you’ll choose a major (the primary subject focus of your degree), which will determine your degree type.
However, there are some instances where you may have a choice of degree, such as a BA or BS in Psychology. In that case, the focus of your program, and to some extent the coursework you take, will depend on the degree you choose to pursue. Psychology majors may choose to pursue a BA if they prefer social work or counseling, or a BS if they enjoy lab research.
Typically, achieving a bachelor's degree is more important than the type of degree you earn. By 2030, 70 percent of job openings could require at least a bachelor’s degree [1].
BA vs. BS degrees: Which is the right fit for me?
When determining whether to get a BA or a BS degree, consider the types of careers you are interested in pursuing. Knowing which paths align with certain majors will be helpful in choosing the right program for you. Here are four areas to consider when making your decision:
1. Majors
Choosing a major can be an exciting step toward your future career. When making your decision, take time to evaluate your interests and values, as well as potential jobs. Some majors are linked to specific career outcomes, such as a computer science degree, while others make it possible to pursue several different types of work, such as a humanities degree. For example, a biology major can become a science writer or teacher, while an education major interested in sustainability can work for a conservation organization or pursue a graduate degree in wildlife conservation.
Questions to ask yourself when choosing a major:
What kind of career industry or field am I interested in?
What skills or work experiences do I have that align with a particular major?
Though not exhaustive, the examples below may help you gain clarity about majors and their potential career fields:
Common BA majors
Humanities (literature, music, religion, philosophy, history, foreign languages)
Business (including museums and institutions)
Education
Media
Visual and performing arts
Social sciences (sociology, anthropology, geography, political science, legal studies)
Non-profit organizations
International development
Government
Social services
Law
Communications, journalism, or media
Business (advertising, sales/marketing, human resources)
Journalism or media
Research
Common BS majors
Natural sciences (biology, environmental science, chemistry, physics)
Health care (medicine, nursing)
Natural resource and sustainability management
Agriculture or food and beverage
Pharmaceuticals
Research and development
Chemical manufacturing
Mathematics and technology (mathematics, statistics, information technology, computer science)
Technology
Information technology
Data science
Engineering (chemical, civil, electrical, mechanical)
Engineering
Manufacturing
Aviation or aerospace
Technology
Common BA or BS majors
These fields frequently have an option for a BA or a BS with slightly different curricula:
Psychology
Social work
Business (marketing and sales)
Research
Education
Primary or secondary education
Non-profit organizations
Business and economics
Banking or finance
Business (from corporations to start-ups)
Governments or think tanks
2. Types of jobs
Your choice of major can lead to many different jobs or industries, depending on what you study. It may be helpful to look up job listings in your chosen field, or search people in similar jobs on LinkedIn to understand the types of degrees and work experiences that led them to that role. For instance, if you're interested in working in finance, looking at job postings can indicate the type of degree typically required.
3. Job industries
It may be helpful to think of industries that excite you. If you enjoy being creative and communicating with others, then you might seek out a BA to help strengthen those skills. However, if you are drawn to more analytical and methodical work, you may choose a BS to refine that training.
Questions to ask yourself when choosing an industry:
What type of degrees and majors do industry leaders earn?
What type of specialization does the industry require for [insert job here]?
Do I need a bachelor’s degree to advance in the industry?
How does my background and interests align with the industry?
The critical thinking and technical skills you can learn during a bachelor’s degree program are often transferable, building a strong foundation for many different industries. However, it is important to know that if you're interested in changing careers in a significant way (such as from nursing to finance), you may need additional training or education in the future.
4. Curricula
Each school's coursework is different. BA degrees tend to have a liberal arts approach, requiring fewer core or major credits and allowing more flexibility to customize your education to your particular interests. In that case, it may be easier to double major or minor in another subject. BS degrees are typically more structured, strictly focused on the major and helping you master the technical skills you'll need for your field.
If you know you want to pursue an advanced degree in the future, that can also help determine what you choose to study now. For example, if you would like to earn a Master's in Public Health (MPH) one day, then opting for a BS in Public Health or a BS in the natural sciences or social sciences might be a good choice.
Questions to ask yourself when choosing a program:
How will this program prepare me for my career goals?
What kind of courses are taught in this program?
Is there opportunity for team projects, mentorship, or career support?

Benefits of earning a BA or BS
Whether you choose to earn a BA or a BS, a bachelor’s degree often leads to higher salaries, lower unemployment, and even greater networking potential. Let's take a closer look at some of the reasons you might choose to pursue your bachelor's:
To open up new career paths
According to a report by the Georgetown Public Policy Institute, an estimated seven out of 10 jobs will require a degree beyond high school by 2030 [1]. With a bachelor's degree, you may be able to explore new careers.
As of 2015, one in three adults earned a bachelor’s degree, making it increasingly likely that you will be vying for a job alongside other applicants with this level of education [2]. Earning a four-year degree can enable you to become marketable to a wider range of fields or industries.
To increase your earning potential
Data shows that workers with higher levels of education earn more and experience lower unemployment rates than those with less education. The difference in earnings is remarkable. On average, those with a bachelor’s degree earn over $25,000 more per year than those with a high school diploma, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) [3].
Engineering, computer science, and math and sciences degrees continue to be the highest earning bachelor’s degrees, according to the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) [4]. If salary is a deciding factor for you, then a BS in any of these majors may be worthwhile.
To switch careers
If you’re ready for a change, a bachelor’s degree in a subject of interest can open new and exciting career paths. Whether you earn your BA or BS, completing a degree demonstrates strong commitment and work ethic. While you do not necessarily need a bachelor's degree to reach your career goals, it could increase the likelihood of being considered for career advancement opportunities.
Hear from Blair, a Coursera learner who pursued a second bachelor's degree as a way to shift to a new career:
“My goal is to launch a career in software engineering. Previously, I was in manufacturing and feeling unfulfilled. The Google IT Support Professional Certificate counted toward my BS in Computer Science at the University of London that I am now enrolled in. The low cost and flexibility of the program allowed me to go back and pursue a second bachelor’s degree.” - Blair Currey, Coursera learner
To build a professional network
Today's job market is competitive. Building a professional network can help you find your next job. Once enrolled in a degree program, you may meet people in your courses, internships, volunteer roles, job fairs, and career development events, all of whom can help grow your network as you expand your career horizons.
To develop skills
Enrolling in a BA or BS program means you have the opportunity to gain skills such as writing, time management, teamwork, and presentation skills, all of which are valuable in the job market. It is an empowering experience because earning a bachelor’s degree is a globally recognized achievement.
What does it take to earn a BA or BS?
Earning a bachelor’s degree is a commitment to learning that may be beneficial to your career, but it also requires resources like time and money.
Time to complete
Both the BA and BS typically take between four and fives years of full-time coursework to complete. A part-time program may take longer. You may be able to finish programs with less rigorous requirements in just three years, particularly if you've earned credits from other programs. BS programs tend to have more required core and major courses than BA programs, and may take more time to complete.
Coursework
Throughout a BA or BS program, you will take core, major, and elective courses. BA degrees provide more room to tailor your education to your interests, whereas BS degrees are more specialized and practical in the subject matter. Curricula are designed to deepen your subject knowledge while expanding on relevant topics. Typically, students are expected to complete a minimum of 120 credits for a bachelor’s degree.
Tuition
Tuition fees for bachelor’s degree programs vary widely by school, as well as by program or major. According to a study at New York University, an estimated 60 percent of public research universities assess tuition based on year of study, major, or both [5]. Schools often charge more for business, engineering, and nursing programs.
This suggests that BS degrees can be more expensive at certain schools. Other schools charge the same for all incoming bachelor’s degree students, no matter their chosen major.
It is important to compare costs for specific programs and whether there are additional costs for books or special equipment (such as art supplies, a laptop, or a software program).
Total fees (including tuition, room and board, and other fees) for the 2021-22 academic year were $26,000 for public institutions, $$55,800 for private non-profit institutions, and $32,900 for private for-profit institutions, according to the National Center for Education Statistics [6]. Online degree programs can sometimes offer a more affordable and flexible option.
Start pursuing a bachelor's degree online today
Take the time to consider whether a bachelor’s degree will help you achieve your career goals, including what subjects interest you and which programs will meet your needs. If you decide a BA or a BS degree is right for you, preparing an application is the next step. Applications typically require a resume, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement.
If you're considering a bachelor's degree, explore these programs from top universities available on Coursera.
Link nội dung: https://khoaqhqt.edu.vn/bachelor-of-arts-a66424.html